
1. v-pre
v-pre 디렉티브를 선언하면 해당 태그는 컴파일되지 않고 그대로 출력됩니다.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="ko"> <head> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script> <script defer src="./main.js"></script> <title>Vue 연습</title> </head> <body> <div id="app" v-pre>{{ message }}</div> </body> </html> |
main.js
const mv = new Vue({ data: { message: 'hello, world!' } }).$mount('#app') |
출력 결과 
v-pre 디렉티브가 없다면 텍스트 보간에 의하여 hello, world!가 출력되어야 하지만, 출력 결과를 확인하면 컴파일 되지않고 {{ message }}가 텍스트 그대로 출력됩니다.
2. v-once
v-once 디렉티브는 일회성 디렉티브 입니다.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="ko"> <head> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script> <script defer src="./main.js"></script> <title>Vue 연습</title> </head> <body> <div id="app" v-once>{{ message }}</div> </body> </html> |
main.js
const mv = new Vue({ data: { message: 'hello, world!' } }).$mount('#app') |
출력 결과를 확인하면 아래와 같이 텍스트 보간에 의하여 hello, world!라는 텍스트가 출력됩니다.
출력 결과 
message를 변경하면 바인딩된 텍스트 메시지도 변경되어야 하지만, v-once 디렉티브의 경우 처음 컴파일된 메시지 상태가 그대로 남습니다.
출력 결과 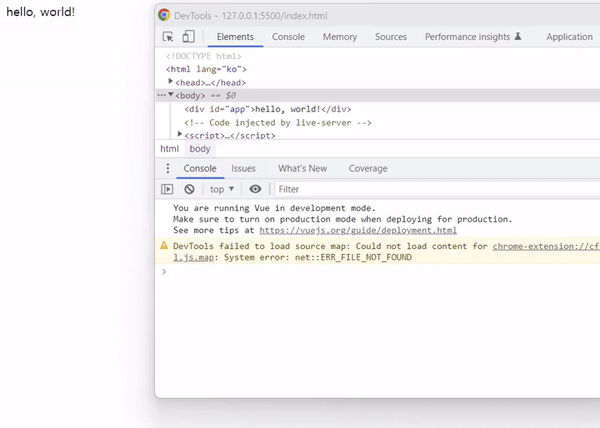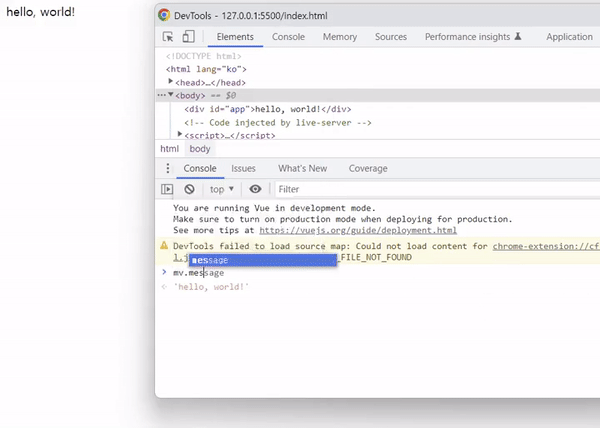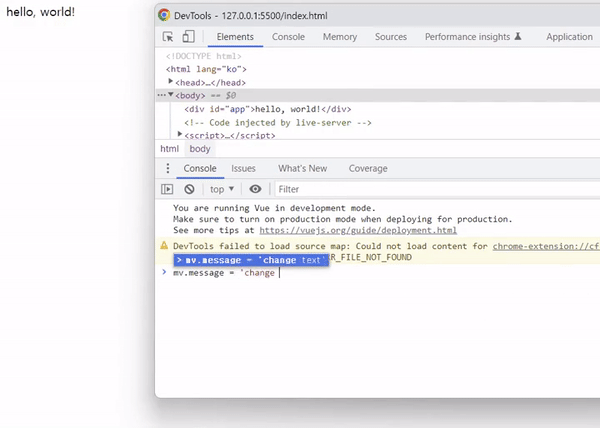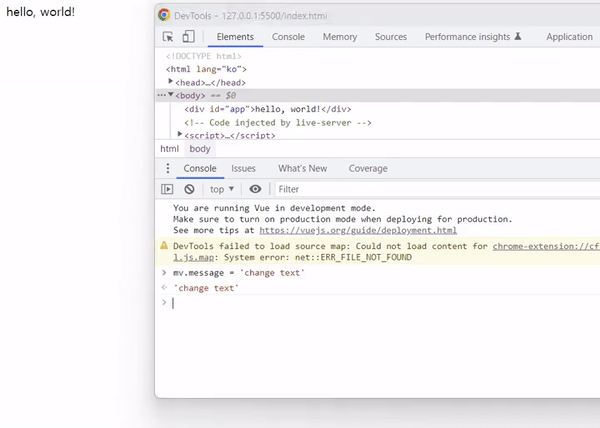
3. v-cloak
v-cloak 디렉티브는 컴파일 되기전 Mustache 태그를 감추기 위해 사용됩니다.
아래와 같이 setTimeout 메소드를 통해 3초후 vue 객체를 생성하고 텍스트 보간을 하겠습니다.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="ko"> <head> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script> <script defer src="./main.js"></script> <title>Vue 연습</title> </head> <body> <div id="app">{{ message }}</div> </body> </html> |
main.js
setTimeout(() => { new Vue({ data: { message: 'hello, world!' } }).$mount('#app') }, 3000) |
아래와 같이 출력 결과를 확인하면 vue 객체가 생성되어 컴파일 되기 전까지 Mustache 태그가 그대로 표시됩니다.
출력 결과 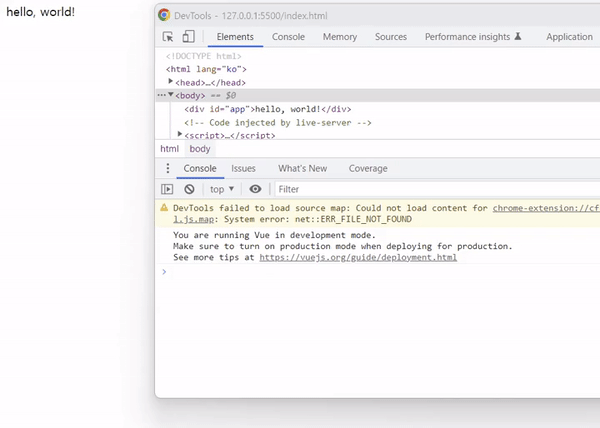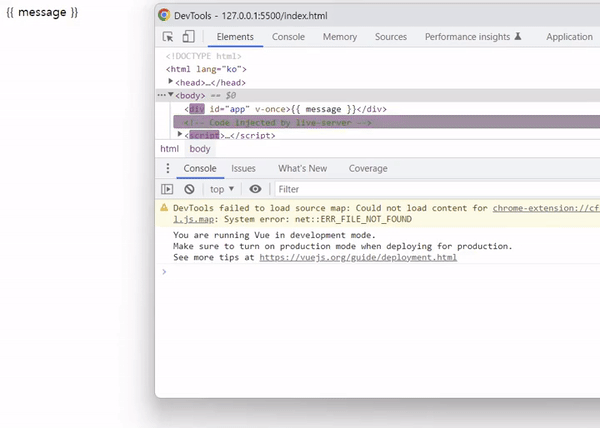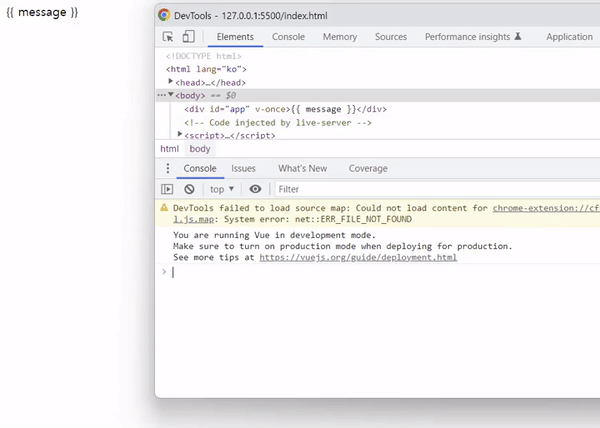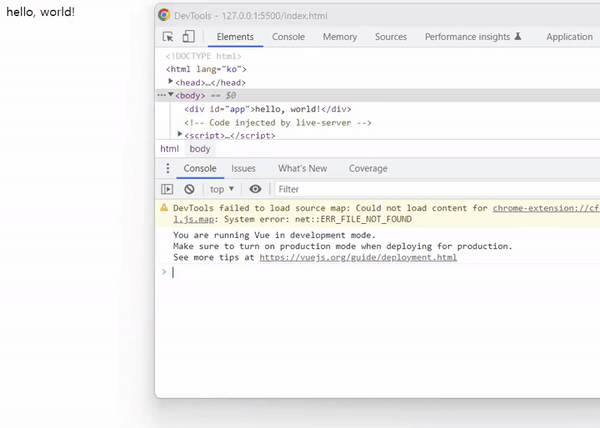
v-cloak 디렉티브는 vue 객체가 컴파일 된 이후 자동으로 제거되기 때문에 v-cloak 속성을 선택자로 하여 display: none; 스타일 속성을 추가하면 됩니다.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="ko"> <head> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script> <script defer src="./main.js"></script> <style> [v-cloak] { display: none; } </style> <title>Vue 연습</title> </head> <body> <div id="app" v-cloak>{{ message }}</div> </body> </html> |
출력 결과 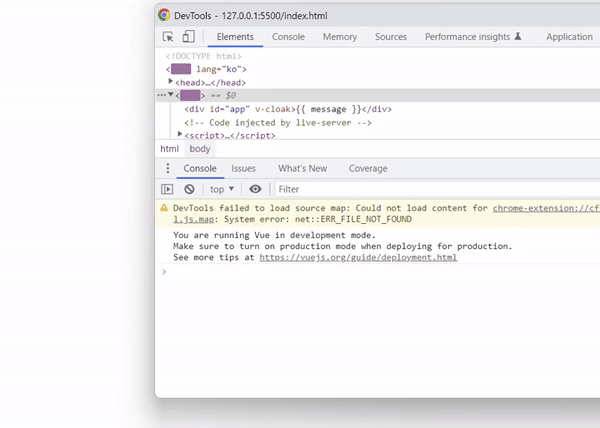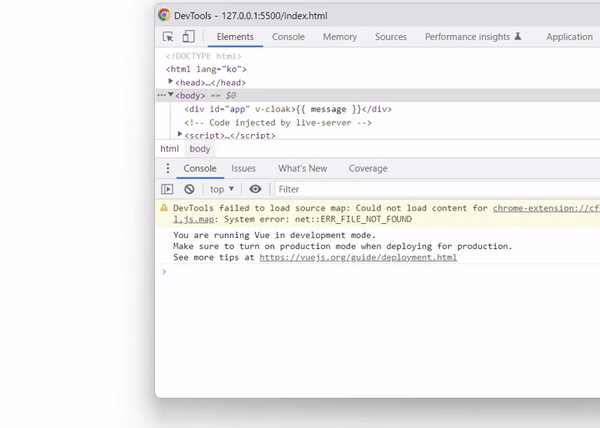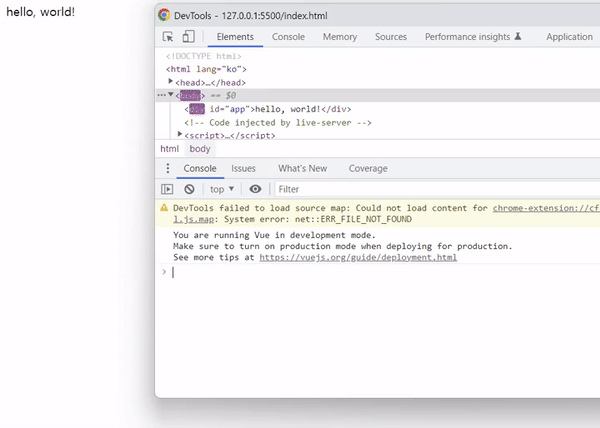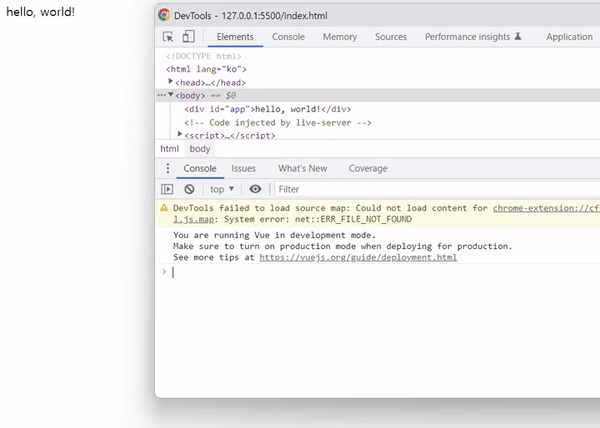
4. v-show
v-show 디렉티브는 v-if 디렉티브와 유사하게 조건문에 대하여 DOM 렌더링 여부를 결정합니다.
하지만 태그 자체를 생성하거나 제거하는 v-if와 달리 v-show는 display 스타일 속성을 통해 렌더링을 결정합니다.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="ko"> <head> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script> <script defer src="./main.js"></script> <title>Vue 연습</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <span v-show="isNotice">{{ notice }}</span> </div> </body> </html> |
main.js
const mv = new Vue({ data: { notice: 'notice', isNotice: true } }).$mount('#app') |
isNotice를 false로 변경하면 태그 자체가 사라지는 것이 아니라 display: none; 스타일 속성이 추가되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
출력 결과 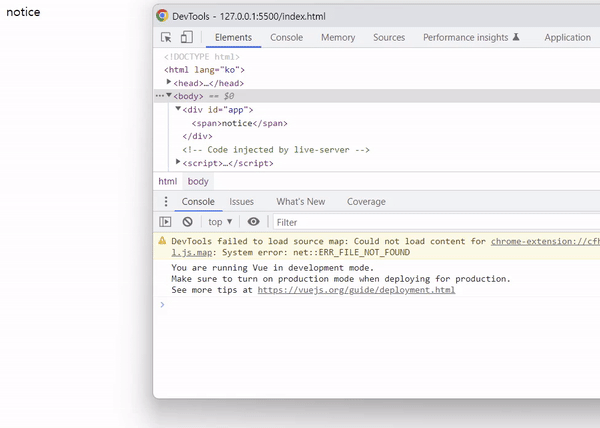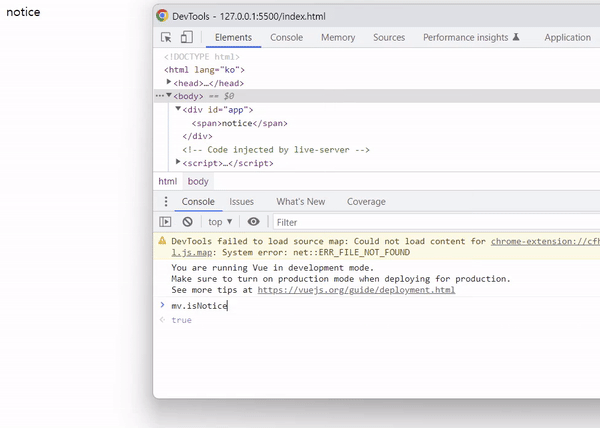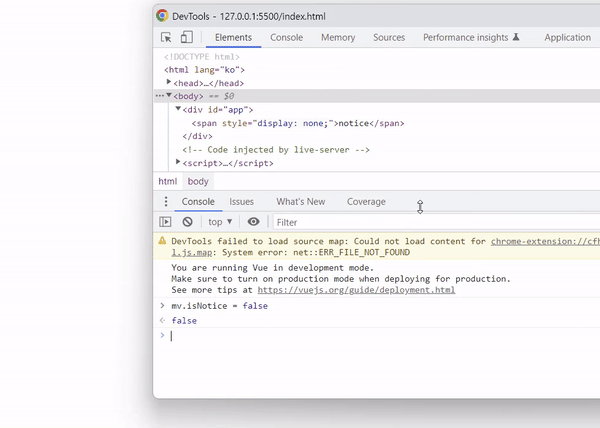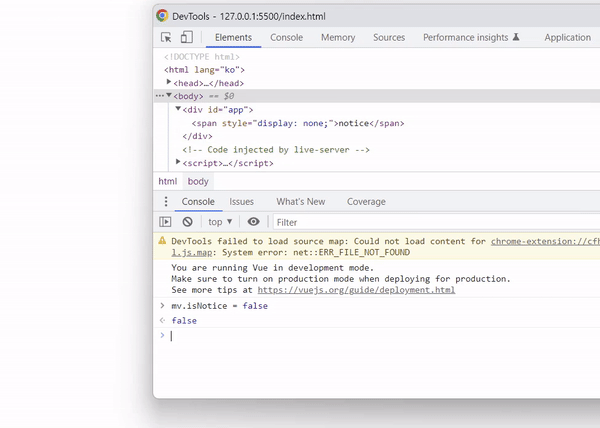
태그 자체를 추가하거나 제거하는 것이 아니기 때문에 조건이 자주 변경된다면 v-if 디렉티브보다 v-show 디렉티브를 사용하는 것이 효율적입니다.
5. v-on
v-on 디렉티브는 이벤트를 연결합니다. 아직 컴포넌트에 대해서 설명하지 않았지만 하위 컴포넌트에서 상위 컴포넌트로의 데이터 전달은 이벤트를 통해 가능합니다.
이벤트는 v-on:[이벤트 이름]="메소드명" 형태로 연결합니다. 클릭이벤트를 연결해보겠습니다.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="ko"> <head> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script> <script defer src="./main.js"></script> <title>Vue 연습</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <div>{{ num }}</div> <button v-on:click="increase">증가</button> <button v-on:click="decrease">감소</button> </div> </body> </html> |
main.js
const mv = new Vue({ data: { num: 0 }, methods: { increase() { this.num++ }, decrease() { this.num-- } } }).$mount('#app') |
각각의 버튼에 대한 클릭 이벤트에 num 데이터를 1 증가시키는 메소드와 1 감소시키는 메소드를 연결했습니다.
출력 결과 
v-on 디렉티브는 v-bind 디렉티브를 : 기호를 통해 선언하는 것처럼 @ 기호를 통해 선언할 수도 있습니다.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="ko"> <head> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script> <script defer src="./main.js"></script> <title>Vue 연습</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <div>{{ num }}</div> <button @click="increase">증가</button> <button @click="decrease">감소</button> </div> </body> </html> |
|  스팟
스팟  스팟
스팟  스팟
스팟  스팟
스팟